BEAST 2 is a cross-platform program for Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of molecular sequences. It estimates rooted, time-measured phylogenies using strict or relaxed molecular clock models. It can be used as a method of reconstructing phylogenies but is also a framework for testing evolutionary hypotheses without conditioning on a single tree topology. BEAST 2 uses Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) to average over tree space, so that each tree is weighted proportional to its posterior probability. BEAST 2 includes a graphical user-interface for setting up standard analyses and a suit of programs for analysing the results.
Download
- VLC reaches 2.0.5 2.0.5 is an important update that fixes some regressions of the 2.0.x branch of VLC. 2.0.5 introduces an important number of fixes for MKV, SWF, AIFF, RTSP, subtitles and encoding. 2.0.5 also improves the Mac OS interface, some video filters and Pulseaudio synchronization.
- The Microsoft.NET Framework version 2.0 (x64) redistributable package installs the.NET Framework runtime and associated files required to run 64-bit applications developed to target the.NET Framework v2.0.
The latest version of BEAST 2 is version 2.6.3. To install this version, select one of the following to download the version for your operating system:
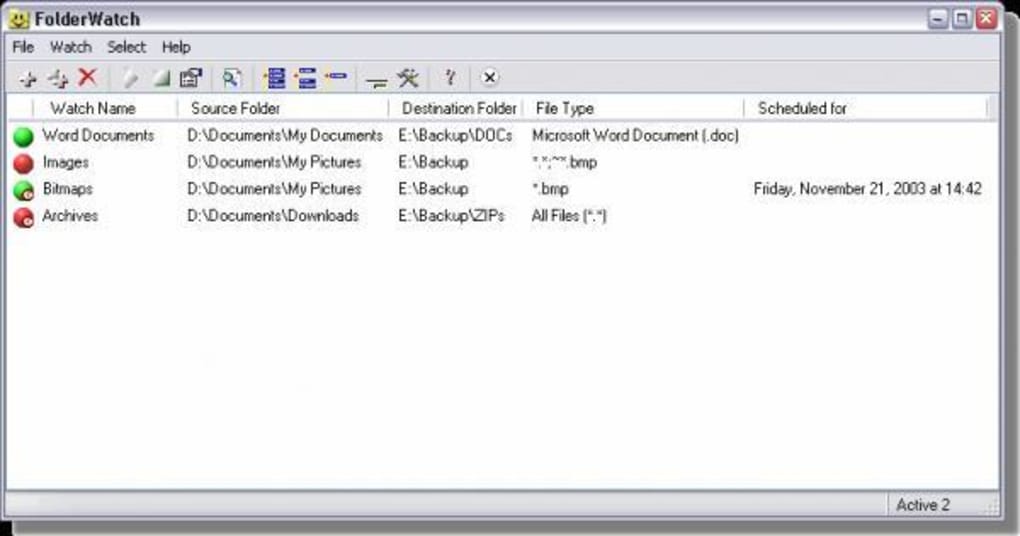
The following VB.NET project contains the source code and VB.NET examples used for Folder Watch. This application allows you to monitor all changes done to the any folder on local or network directory.
- Download for Windows without java (8MB) /with java (45MB)
- Download for Mac OS X without java (8MB) /with java (46MB)
- Download for Linux without java (8MB) /with java (47MB)
Alternatively, if you already have v2.6.X (X=0, 1 or 2) installed, you can upgrade via the package manager.
If you download a version of BEAST without Java, you need to install Java separately (for OS X, JDK 8 is recommended). BEAST requires Java version 8 or higher.Older versions are available from the BEAST2 releases web page.
The BEAST 2 source code is available from the GitHub repository, which produces the latest cutting edge jar file here: beast.jar.
XML reference
The XML reference is available in the online manual.
Previous releases and version history
Previous releases and version history are available on the BEAST2 releases web page.
Version 2
BEAST 2 is a rewrite of BEAST 1.x, placing a greater emphasis on modularity. This makes it easier to extend BEAST 2 via its package system. As a result, BEAST 2 has rapidly acquired the ability to perform a diverse array of model-based analyses. For a comparison of features/models currently available in BEAST 2 with those currently implemented in BEAST 1, refer to this features table.
Getting Started
As BEAST 2 is such a large and complicated application, first-time users may find coming to grips with the program and its capabilities a daunting task. We therefore encourage you to perform the following:
- Familiarise yourself with the terminology used by BEAST 2 users and developers.
- Work through the available tutorials, particularly those applicable to your data.
- Join the users mailing list by visiting the beast-users group or sending an email to beast-users+subscribe@googlegroups.com. This list is used to announce new versions and to advise users about bugs and other problems.
- Attend the Taming the BEAST workshop.
After completing these introductory steps, you’ll be well equipped to dive into the BEAST 2 Book.
BEAST 2 Packages
In BEAST 2, many models and analysis methods are implemented as BEAST 2 Packages. This means that the package is developed and maintained separately to BEAST 2 itself. To access these methods, you must download the corresponding packages in addition to BEAST 2. This is made easy by the BEAST 2 Package Manager, which is part of BEAST 2’s graphical user interface. See the Managing Packages page for details.
A list of known currently-available packages is provided in the BEAST 2/BEAST 1 feature comparison table.
Dealing with Problems and Performance Issues
While we aim to make using BEAST 2 a pleasant experience, problems do sometimes arise. In such cases, the following, please review the following information:
- An explanation of error messages and their meanings.
- The list of frequently asked questions (FAQ).
For performance-related issues, refer to this handy list of suggestions for improving performance.
Package Development
BEAST 2 is designed to be extended. Prospective package developers should refer to the Package Development Guide.
Who develops BEAST?
BEAST 2 is developed by a team of scientists around the world. This web site is managed by the Centre for Computational Evolution.
Deploy code with rsync over ssh, using NodeJS.
NodeJS version is more than a minute faster than simple Docker version.
This GitHub Action deploys specific directory from GITHUB_WORKSPACE to a folder on a server via rsync over ssh, using NodeJS.
This action would usually follow a build/test action which leaves deployable code in GITHUB_WORKSPACE, eg dist;
Pass configuration with env vars
1. SSH_PRIVATE_KEY [required]
Private key part of an SSH key pair.The public key part should be added to the authorized_keys file on the server that receives the deployment.
More info for SSH keys: https://www.ssh.com/ssh/public-key-authentication
The keys should be generated using the PEM format. You can use this command
2. REMOTE_HOST [required]
eg: mydomain.com
3. REMOTE_USER [required]
eg: myusername
4. REMOTE_PORT (optional, default '22')
eg: '59184'
5. ARGS (optional, default '-rltgoDzvO')
For any initial/required rsync flags, eg: -avzr --delete
6. SOURCE (optional, default ')
The source directory, path relative to $GITHUB_WORKSPACE root, eg: dist/
7. TARGET (optional, default '/home/REMOTE_USER/')
The target directory
Folderwatch V2 0 5 Percent
!!! Please use latest version, Readme file is just an example, eg: ssh-deploy@v2.1.5
Folderwatch V2 0 5 0
Disclaimer
(0 5) On A Graph
Check your keys. Check your deployment paths. And use at your own risk.