Last Updated on January 8, 2019 by
G 1.7 0.9
Networking Essentials Chapter 1-5 Checkpoint Exam Answers Full 100% 2019
Pdf Checkpoint 1 9 7 0 5
Security update available in 3D Plugin Beta 9.7.0.29430. Release date: September 29, 2019. Platform: Windows. Foxit has released 3D Plugin Beta 9.7.0.29430 for Foxit Reader and PhantomPDF, which addresses potential security and stability issues. Affected versions. Microsoft Windows. CIS Cisco Wireless LAN Controller 7 Benchmark v1.1.0. CIS Check Point Firewall Benchmark v1.1.0. 16 Chapter 7: Rational Expressions and Equations—Checkpoint 1—Solutions DO NOT COPY. Simplify each expression. A) b) 3x - 27 x 2- 1 # x2 - 7x - 8 x - 81 5x 2x - 2 2a2b 9ab3 4bc2. 7/0.2mm 0.22 mm² 24 AWG 6A 1.62 mm 19/0.15mm 0.338 mm² 22 AWG 8A 1.67 mm 19/0.2mm 0.597 mm² 20 AWG 11A 1.92 mm Description/Reel Size Manufacturers Farnell. Check Point’s Enterprise Support Lifecycle policies outline the product support guidelines for a product’s lifecycle. The objective of this policy is to standardize and normalize product lifecycle practices to assist you in making an informed purchase, and support and upgrade decisions.
What is an example of a binary value from everyday life?
- room temperature
- a simple light switch
- speed of a traveling car
- brightness of a light bulb
Explanation: A binary digit (or bit) has two possible values, 0 or 1. The on and off state of a simple switch is an example of the two states represented by a bit.
Which wireless technology is used on smart phones to transmit data to another device within only very close proximity?
- NFC
- Wi-Fi
- 3G/4G
- Bluetooth
Explanation: Near Field Communications (NFC) is a wireless technology that enables data to be exchanged by devices that are in very close proximity to each other.
Which two devices are shared peripherals? (Choose two.)
- tablet
- laptop
- scanner
- printer
- touch-pad with digital stylus
Explanation: A shared peripheral device does not connect directly to a network. This device is attached to a host (such as a PC) and the host connects to the network to share the peripheral device.
Which three configuration components are required to allow a host to communicate with other hosts on remote networks? (Choose three.)
- IP address
- DNS server
- subnet mask
- domain name
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
Explanation: An IP address, a subnet mask, and a default gateway are required on a host that must communicate with another host in a remote network. DNS server information is needed if mapping a domain name to an associated IP address. DHCP server information is dynamically learned and is not a required configuration for remote network reachability.
Which three factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate network media? (Choose three.)
- the speed of the CPU and amount of memory in servers
- the environment in which the media is installed
- the data security and fault tolerance requirement
- the amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
- the distance between hosts that the media will connect
- the operating systems used on network devices in the network
Explanation: Several criteria should be considered when selecting network media:The cost of the media and installation
The environment in which the media is installed
The amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
The distance between hosts that the media will connect
Which factor classifies a host as a server?
- the CPU speed
- the software installed
- the amount of memory
- the network connection
Explanation: A server is a host with server software installed. Although CPU, memory, and the network connection will determine the performance of a server, it is the server software that provides desired server services.
Which two types of interference may affect the data throughput on UTP cables? (Choose two.)
- EMI
- noise
- moisture
- crosstalk
- temperature
Explanation: Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling is sensitive to the interference introduced by electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
Which statement defines a data communications protocol?
- an alliance of network device manufacturers
- a set of rules that govern the communication process
- a set of product standards for types of network devices
- an exchange agreement of network devices among vendors
Explanation: A data communication protocol is a set of rules that govern the communication process.
Which statement describes a MAC address?
- It is 128-bits in length.
- It contains two portions, the network portion and the host portion.
- It is a physical address assigned to an Ethernet NIC by the manufacturer.
- It identifies the source and destination addresses of hosts on the Internet.
Explanation: The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a physical address assigned to each Ethernet NIC by manufacturers. It is 48-bits in length. The MAC address is used to identify the source and destination on a local Ethernet network. It cannot be routed to remote networks.
What information does an Ethernet switch examine and use to build its address table?
- source IP address
- source MAC address
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
Explanation: An Ethernet switch examines the source MAC address of an incoming frame. If the source MAC address is not in the MAC address table, the switch will add it to the table with the associated ingress Ethernet port.
What is the equivalent decimal value given a binary number of 11001010?
- 196
- 202
- 212
- 240
Explanation: The equivalent decimal value for a binary number of 11001010 can be determined by 1*2^7+1*2^6+1*2^3+1*2^1.
What is the difference between the terms bandwidth and throughput?
- Bandwidth is measured with Mb/s and throughput is measured in Kbps.
- Bandwidth is the capacity of data transfer in a network and throughput is the actual data transfer rate.
- Bandwidth measures data transfer of web applications and throughput measures data transfer of video applications.
- Bandwidth represents the data transfer rate in a local network and throughput represents the data transfer rate over the Internet.
Explanation: Both bandwidth and throughput are the measurement of data transfer over a period of time. They use the same measurement units. However, bandwidth is used to indicate the theoretical capacity of a network connection whereas throughput is used to indicate the actual data transfer rate between two hosts at the time of measurement.
Which three IP addresses are considered private addresses? (Choose three.)
- 10.234.2.1
- 128.37.255.6
- 172.17.254.4
- 172.68.83.35
- 192.168.5.29
- 198.168.6.18
Explanation: The designated private IP addresses are within the three IP address ranges:10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
Which IP address is a unicast address if a default subnet mask is used?
- 201.34.45.0
- 192.16.43.67
- 226.34.15.78
- 195.124.45.255
Explanation: The IP addresses 201.34.45.0, 192.16.43.67, and 195.124.45.255 are Class C addresses. With the default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, 192.16.43.67 is a unicast address or host address, 195.124.45.255 is a broadcast address, and 201.34.45.0 is a network address. IP address 226.34.15.78 is a Class D multicast address.
What is the full uncompressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:DB8:0:0:AA::200?
- 2001:0DB8:0000:0000:00AA:0000:0200:0000
- 2001:DB80:0000:0000:AA00:0000:0000:0200
- 2001:0DB8:0000:0000:00AA:0000:0000:0200
- 2001:0DB8:0000:00AA:0000:0000:0000:0200
Explanation: An IPv6 address is made up of 128 bits represented in hexadecimal numbers.There are two rules that help reduce the number of digits needed to represent an IPv6 address.Rule 1 – Omit leading zeros in any 16-bit section.
Rule 2 – Replace any single group of consecutive zeros with a double colon (::). This can only be used once within an IPv6 address.
A user types www.cisco.com into a web browser to visit the corporate website. Which service will resolve the domain name to an associated IP address?
- FTP
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
Explanation: When a user types a domain name to visit a website, the DNS service is called to resolve the domain name to its associated IP address before the user packet is sent to the website.
A user opens multiple windows on the desktop with several tasks including web surfing, emailing, and Skype calling. What is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack to track the specific sessions for each application?
- port number
- destination IP address
- Hypertext Markup Language
- domain name to IP address resolution
Explanation: A user may request different services from the same server or different servers. TCP and UDP port numbers are used to keep track of specific sessions between a client and server.
Which two application layer protocols manage the exchange of messages between a client with a web browser and a remote web server? (Choose two.)
- DNS
- HTTP
- HTML
- DHCP
- HTTPS
Explanation: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and HTTP Secure (HTTPS) are two application layer protocols that manage the content requests from clients and the responses from the web server. HTML (Hypertext Mark-up Language) is the encoding language that describes the content and display features of a web page. DNS is for domain name to IP address resolution. DHCP manages and provides dynamic IP configurations to clients.
A client is sending a message to request information from a web server on the Internet. Which parameter is used in the message to indicate the specific service requested?
- source port
- destination port
- server domain name
- destination IP address
Explanation: When clients send requests for a service from a server, the destination port number is used to indicate the specific service requested.
How much data can be encapsulated into a normal sized Ethernet frame before it is sent over the network?
- 0 to 1024 bytes
- 32 to 1500 bytes
- 46 to 1500 bytes
- 64 to 1518 bytes
Explanation: According to the Ethernet standards, each Ethernet frame can carry 46 to 1500 bytes of user data. During the encapsulation process, other fields are added, such as destination MAC address, source MAC address, and FCS. The size of Ethernet frames is normally limited to a maximum of 1518 bytes and a minimum of 64 bytes.
Which transport layer protocol provides best effort delivery without guaranteeing that packets arrive at the destination?
- SSH
- TCP
- UDP
- HTTP
Explanation: User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a best effort transport layer protocol. Unlike TCP, it does not use an acknowledgment protocol to ensure reliable packet delivery. TCP provides reliable delivery service. HTTP and SSH are application layer protocols in the TCP/IP model.
Which scenario describes a peer-to-peer network?
- Users access shared files from a file server.
- A user visits a webpage on the company web site.
- A user has shared a printer attached to the workstation.
- Users print documents from a network printer that has a built-in NIC.
Explanation: In a peer-to-peer network there is no centralized or dedicated server. A user computer can be a client to request service from another user computer and a server to share a network resource (such as a printer) to other users.
Which three devices are considered intermediate devices in a network? (Choose three.)
- router
- server
- switch
- workstation
- network printer
- wireless access point
Explanation: Intermediate devices in a network provide network connectivity to end devices and transfer user data packets during data communications.
When a host sends a packet, how does it determine if the destination of the packet is on the same local network or on a remote network?
- It checks to see if the default gateway is configured.
- It compares the source and destination MAC addresses.
- It queries the DNS server with the destination IP address.
- It uses the subnet mask to compare the source and destination IP address.
Explanation: When a host sends a packet, it uses the subnet mask to compare the source IPv4 address and the destination IPv4 address. If the network bits match, both the source and destination host are on the same local network. Otherwise, the destination host is on a remote network.
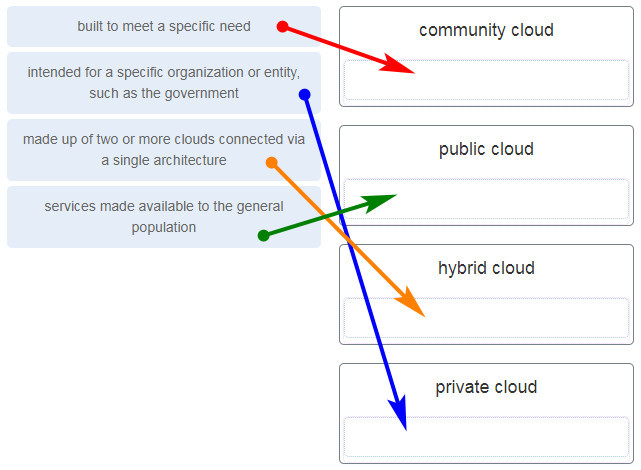
Match the TCP/IP model layer to the function.
Networking Essentials Chapter 1-5 Checkpoint Exam Answers 01
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
What is the code displayed on the web page?
Networking Essentials Chapter 1-5 Checkpoint Exam Answers 02
Networking Essentials Chapter 1-5 Checkpoint Exam Answers 03
- Correct
- Success
- Welldone
- Configured Right
Explanation: The IP address configuration on PC0 requires the following:IP address – any valid host address on the LAN, except for .254
Subnet mask – default value for the network
Gateway – the nearest router interface
DNS – the DNS server on the ISP network